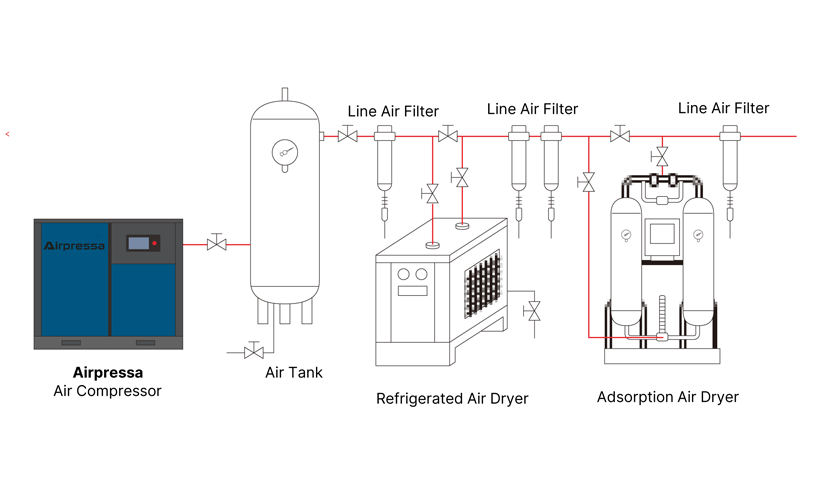
An industrial air compressor package is a comprehensive system that combines an air compressor with various ancillary components into one integrated unit.
Such packages typically include the main compressor, air treatment devices (such as refrigerated or desiccant dryers), air receiver tanks, filters, piping networks, and control systems.
Designing an integrated system requires a detailed understanding of the compressor’s performance, supporting components, and system requirements. This article explains the step‐by‐step process for designing an industrial air compressor package.
You can click on any section that you interest to get there quickly.
Key Components of an Air Compressor Package
1. The Air Compressor Unit
At the heart of the package is the air compressor. Industrial systems often use rotary screw compressors due to their efficiency, reliability, and capacity for continuous operation.
Models may range from 7.5 kW to 250 kW (approximately 10 hp to 350 hp), delivering airflow from about 1.0 m³/min (35 CFM) to 40 m³/min (1400 CFM). Options include:
Oil Lubricated Screw Compressors: These offer efficient sealing and heat dissipation through lubricating oil. They suit high-demand applications in heavy industries.
Oil-Free Screw Compressors: Essential for applications that require contamination-free air, such as electronics manufacturing or food processing.
Variable Speed Drive (VSD) Compressors: VSD technology enables the compressor to adjust its speed according to air demand, improving energy efficiency.
Specialized Models: Products such as laser dedicated or low-pressure and high-pressure screw compressors meet niche requirements, delivering operating pressures from 6 bar up to 40 bar.
Click to check Airpressa various Screw Air Compressor models.
2. Air Treatment System
Compressed air often contains moisture and contaminants that can adversely affect downstream equipment. Air treatment is therefore a vital component. The two primary types include:
Refrigerated Air Dryers: These cool the air, condense moisture, and remove water from the stream. They are effective in applications where moderate moisture removal is acceptable.
Desiccant Air Dryers: These systems use desiccant materials to absorb water vapor, providing extremely dry air. They are suitable for processes that require minimal moisture content.
3. Air Receiver Tanks
Air receiver tanks act as buffers, storing compressed air and reducing the frequency of compressor cycling. The tank size is chosen based on the total CFM output and the system’s transient response requirements.
A larger tank size helps maintain a consistent pressure, particularly during peak load periods, and extends the compressor’s operating life by reducing on/off cycles.
4. Air Filters
Air filters ensure that particulate matter, oil, and other contaminants are removed from the compressed air. High-efficiency filters protect downstream tools and improve the overall quality of the air supplied by the package.
Depending on the application, multi-stage filtration may be necessary.
5. Piping and Distribution Networks
The design of the piping system must minimize pressure drop and distribute air evenly to all end-use points. Piping should be sized appropriately, with considerations for material, length, and layout, to maintain system efficiency.
6. Control Systems and Monitoring
Modern air compressor packages incorporate sophisticated control systems that regulate compressor operation, monitor performance, and manage fault conditions.
These control systems may include programmable logic controllers (PLCs), remote monitoring capabilities, and variable frequency drives (VFDs) for VSD compressors.
They offer real-time data on parameters such as pressure, temperature, and airflow, enabling proactive maintenance and system optimization.
Air Compressor Package Design Considerations
Understanding System Requirements
A successful design begins with a clear understanding of the application requirements. Critical parameters include:
Airflow (CFM or m³/min)
Determined by the combined demand of the air tools and processes. For instance, in a manufacturing plant where several pneumatic tools operate simultaneously, the design must accommodate peak airflow needs.
Operating Pressure (Bar or PSI)
The system must deliver air at the pressures required by end-use applications. Different processes may require pressures ranging from 6 bar for light-duty tasks to over 40 bar for specialized applications.
Duty Cycle and Operating Time
Continuous operations require compressors with high duty cycles, while intermittent processes may allow for lower cycle ratings. Knowing the operating schedule helps in selecting a compressor that can handle extended run times without overheating.
Sizing the Compressor
The compressor’s capacity should be matched to the calculated demand. This calculation typically involves:
Summing the CFM Requirements
Identify each tool’s airflow consumption and add them together.
Applying a Safety Margin
Increase the total by 25–30% to account for inefficiencies, leaks, and future expansion.
Matching Pressure Requirements
Choose a compressor that exceeds the maximum PSI or bar requirement of the tools in use.
A properly sized compressor ensures that the system operates within its design limits, reducing energy waste and preventing premature component wear.
What Size Air Compressor Do I Need? Step by Step
A correctly size air compressor not only supplies sufficient airflow for your tools but also minimizes energy waste and unnecessary downtime.
This guide explains the fundamental specifications of air compressors and provides step-by-step instructions on how to calculate the appropriate size.
Integration of Auxiliary Components
In an integrated air compressor package, every component must be chosen to work in harmony with the others. Consider the following:
Air Dryers and Filters
Select air treatment units based on the moisture and contaminant load expected in the application. The combination of refrigerated and desiccant dryers may be used in tandem to achieve the desired air quality.
Air Receiver Tanks
The air tank’s capacity should be determined based on both the airflow and the variability of the demand. Larger tanks offer smoother operation but require more space.
Piping Layout
The piping network must be designed to minimize pressure drops. Use of insulated piping may be required in cold environments to prevent condensation.
Control and Monitoring
A centralized control system that manages compressor start/stop, monitors pressure and temperature, and triggers alarms in case of faults is vital for maintaining system reliability.
Thermal Management
Compressors generate significant heat during operation. Effective thermal management is crucial to avoid overheating and maintain performance. Design considerations include:
Cooling Systems
Incorporate air or liquid cooling systems as needed. Oil lubricated compressors benefit from oil cooling systems, whereas oil-free systems may require additional cooling measures.
Heat Exchangers
In some cases, external heat exchangers are used to dissipate heat more efficiently.
Ventilation
Ensure that the compressor package is installed in an area with adequate airflow to prevent heat buildup.
Energy Efficiency
Energy consumption is a critical factor in industrial operations. Improving energy efficiency not only lowers operating costs but also reduces environmental impact. Methods to enhance efficiency include:
Variable Speed Drives
VSD compressors adjust motor speed based on demand, reducing energy use during low-load conditions.
Optimized Control Algorithms
Modern control systems can optimize compressor cycles and minimize unnecessary operation.
Heat Recovery Systems
In some designs, the heat generated by the compressor can be recovered and used for other processes, improving overall plant efficiency.
What is the VSD Compressor and How to Choose Correctly
VSD compressor is a cutting-edge technology that has gained significant traction in recent years.
These advanced compressors have revolutionized the way compressed air is generated, offering unmatched energy-saving capabilities, flexibility, and control.
The VSD compressor has become a game-changer in the field of air compression, powering the modern-day industry. But what exactly is a VSD compressor, and how do you choose the right one for your business?
Safety and Compliance
Safety must be integrated into every aspect of the design. Key areas to address include:
Pressure Relief Systems
Install safety valves and pressure relief devices to protect the system from over-pressurization.
Electrical and Mechanical Safety
Ensure that all electrical components meet local safety standards and that moving parts are adequately guarded.
Environmental and Emission Standards
Design the system in accordance with local and international regulations, particularly for systems using diesel or gas-powered compressors.
Maintenance Accessibility
The layout should allow easy access to components for routine maintenance and repairs, reducing downtime.
Integration and Compressor System Layout
Designing the System Layout
The layout of an industrial air compressor package must consider both functional and spatial requirements. A well-planned layout improves operational efficiency and simplifies maintenance.
Modular Design
A modular approach enables customization and scalability. Components can be added or replaced as requirements change.
Compact Integration
Combining the compressor, dryer, tank, filters, and control panel in a compact, well-organized enclosure minimizes the footprint and simplifies installation.
Piping and Cabling Routes
Plan for optimal routing of air pipes and electrical cables to avoid interference and ensure ease of service.
Balancing Performance and Space Constraints
Industrial facilities may have limited space. The challenge is to design an air compressor package that meets performance targets while fitting within the available area. Consider the following:
Vertical Versus Horizontal Configurations: Vertical designs may offer space-saving advantages, while horizontal configurations can provide easier access for maintenance.
Mobile Solutions: In scenarios where space is at a premium or the system needs to be relocated frequently, mobile air compressor packages with integrated wheels or lifting mechanisms are preferred.
Footprint Optimization: Use computer-aided design (CAD) tools to simulate the layout and optimize the arrangement of components for maximum efficiency and minimal spatial impact.
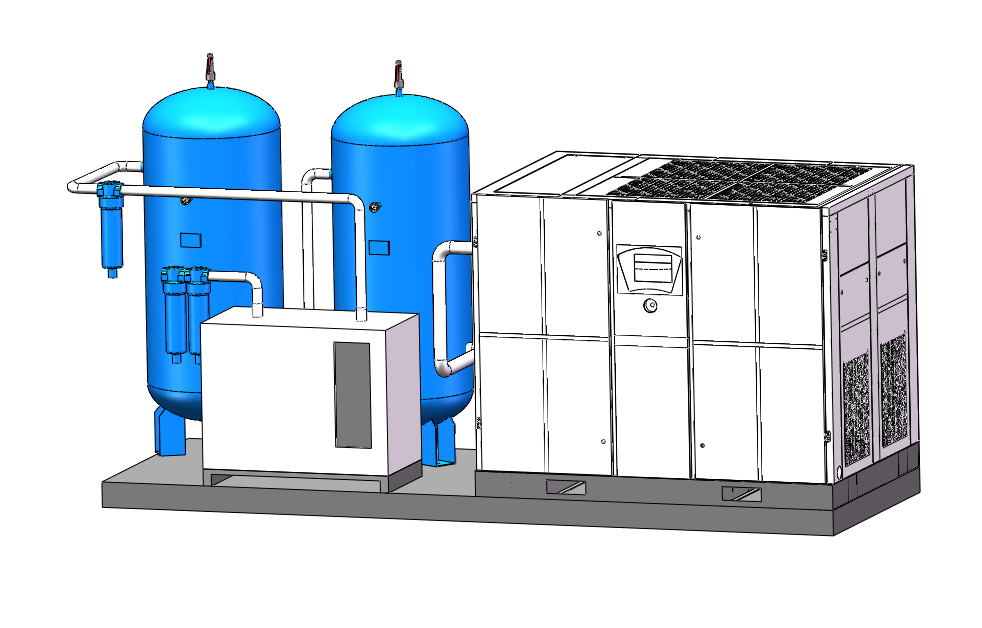
Airpressa Compressed Air System Design
Airpressa provides complete compressed air systems, including air compressors, air dryers, air tanks, and air filters. And we provide more flow options 7.5kw (10hp) – 250 kw (350hp), in order to meet the choice of most industries and customers.
Control Systems and Monitoring
Modern industrial air compressor packages employ sophisticated control systems to enhance performance and reliability. These systems should include thises functions:
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs)
PLCs provide centralized control of compressor operation, monitor critical parameters, and automate start/stop cycles based on demand.
Remote Monitoring
Integration of remote monitoring capabilities enables real-time data acquisition and analysis. Operators can access system performance data from a central control room or remotely via the internet.
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs)
VFDs adjust the compressor motor speed in response to changes in air demand. This technology improves energy efficiency and maintains consistent pressure.
Data Logging and Alarms
Continuous data logging helps track performance trends, while alarms notify operators of any deviations from normal operating conditions.
Ensuring System Reliability
A reliable control system is critical for minimizing downtime and ensuring safe operation. Design measures include:
Redundancy:
Incorporate redundant sensors and control circuits to maintain functionality in the event of a component failure.
User-Friendly Interfaces:
Provide intuitive interfaces that display critical information clearly. This ensures that operators can quickly diagnose issues and perform necessary adjustments.
Preventive Maintenance Alerts:
The control system should generate maintenance alerts based on runtime and performance data. This proactive approach helps reduce the risk of unexpected breakdowns.
Air Compressor Package Application Examples
Designing an air compressor package involves tailoring the system to the specific needs of the industry. Consider these examples:
Automotive Manufacturing
An automotive assembly line may require a compressor package capable of delivering 20–30 m³/min (700–1050 CFM) at pressures of 8–10 bar.
The package might include a VSD screw compressor paired with refrigerated air dryers and a large air receiver tank. This configuration ensures that pneumatic tools such as impact wrenches and spray systems receive a stable and continuous supply of air.
Food and Beverage Processing
In food production, air quality is critical, the pure air of an oil-free air compressor can better meet the demand.
An oil-free screw compressor package operating at around 8–10 bar with a moderate airflow of 10–15 m³/min (350–525 CFM) can be combined with desiccant air dryers and high-efficiency filters. This design guarantees that the compressed air remains free from oil and contaminants.
Electronics Manufacturing
Precision processes in electronics also require extremely clean and stable air. A compact air compressor package with a low airflow requirement (around 10–20 m³/min or 350–700 CFM) at pressures near 8 bar may be sufficient.
Integration of an oil-free compressor, desiccant dryer, and advanced monitoring system ensures high-quality air without compromising on efficiency.
Construction and Heavy Industrial Applications
For construction sites or heavy industrial operations such as mining, the compressor package might need to deliver high airflow (up to 40 m³/min or 1400 CFM) at pressures up to 25 bar or more, it needs heavy industrial air compressor like 250 kw even more.
In addtition, the diesel air compressors are common in these applications due to their durability and portability. A robust control system and safety features are incorporated to withstand harsh operating conditions.
Tailoring the Design for Specific Applications
The design of an air compressor package must take into account the unique requirements of each industry.
For instance, in aerospace applications, reliability and precision are paramount. The compressor package must deliver consistent airflow at precise pressure settings, and redundancy in control systems is critical.
In contrast, general manufacturing facilities may prioritize energy efficiency and ease of maintenance, leading to a preference for VSD screw compressors with modular designs.
What Types of Air compressor? The Complete List
There are many types of air compressor, positive and dynamic air compressors are two main types, each with its own advantages and applications.
Positive air compressors rely on positive displacement to deliver a continuous flow of compressed air, while dynamic air compressors use high-speed impellers to achieve compression.
Understanding the differences between these compressor types can help industries choose the most suitable comp1ressor for their specific needs.
Conclusion
Designing an industrial air compressor package is a multifaceted engineering task that requires careful evaluation of system requirements, component integration, and performance optimization.
The process begins with a thorough assessment of the end-use applications. Calculating the total CFM requirement with an added safety margin ensures that the compressor can handle peak loads and potential future expansion.
Matching these requirements with the appropriate compressor type – whether it is an oil lubricated, oil-free, or VSD screw compressor.
Auxiliary components such as air dryers, filters, receiver tanks, and piping networks must be integrated seamlessly into the package.
Moreover, Advanced control systems play a vital role in managing operation, ensuring safety, and enhancing energy efficiency through features like variable frequency drives and remote monitoring.
And last but not least, safety and regulatory compliance should be integrated throughout the design.
From pressure relief valves and emergency shutdown mechanisms to meeting electrical and environmental standards, every aspect of the package is engineered to protect both operators and equipment.